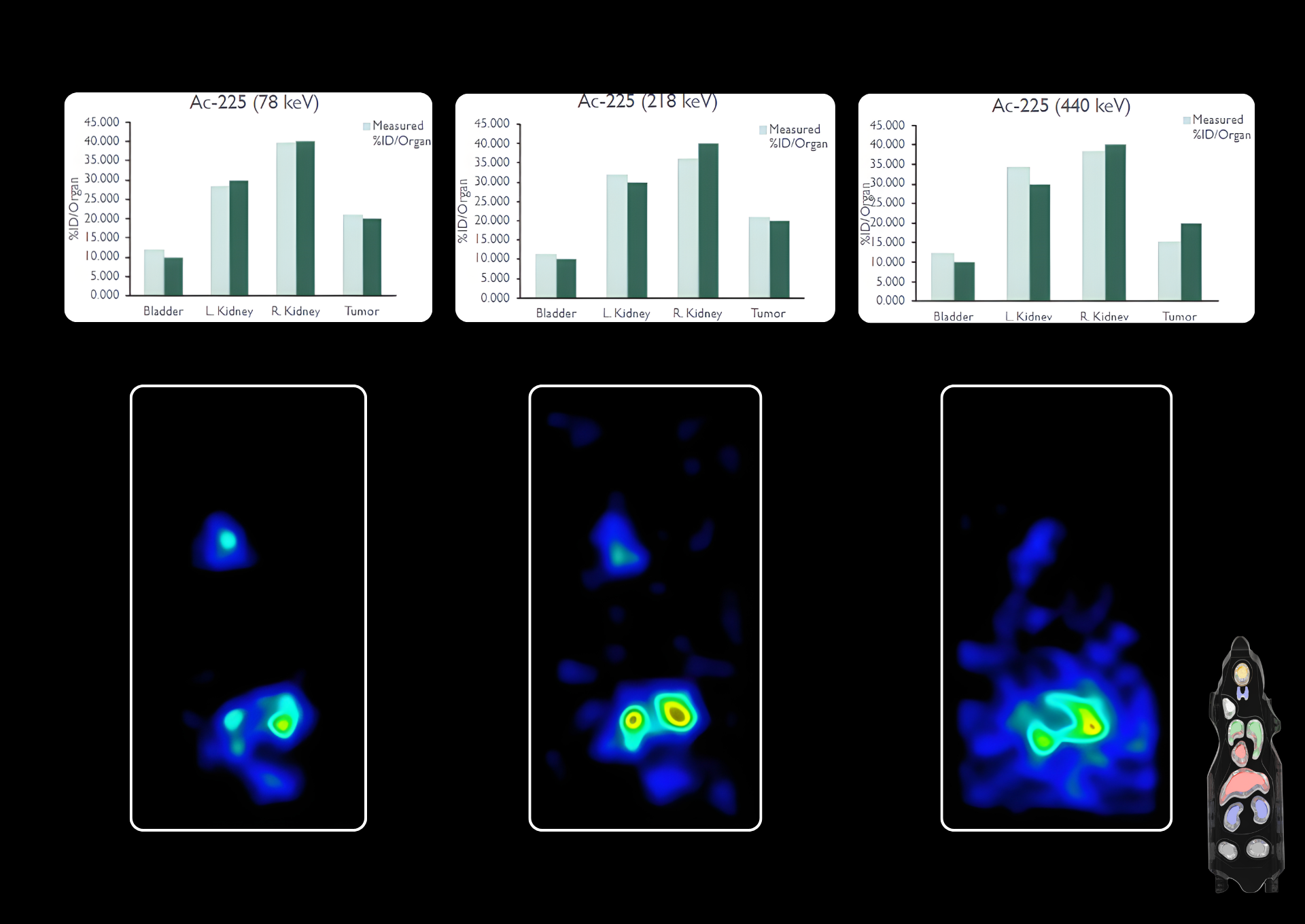
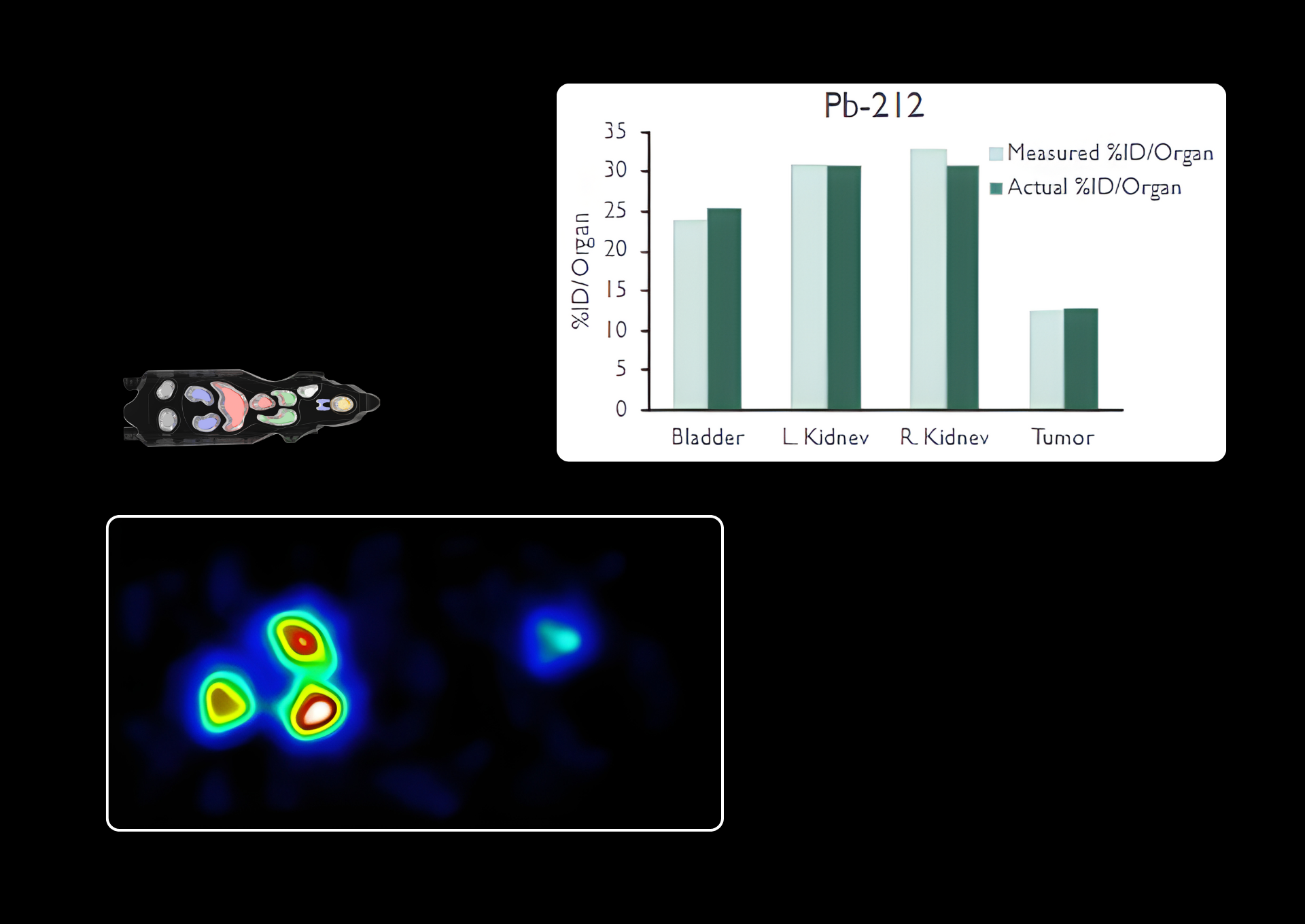
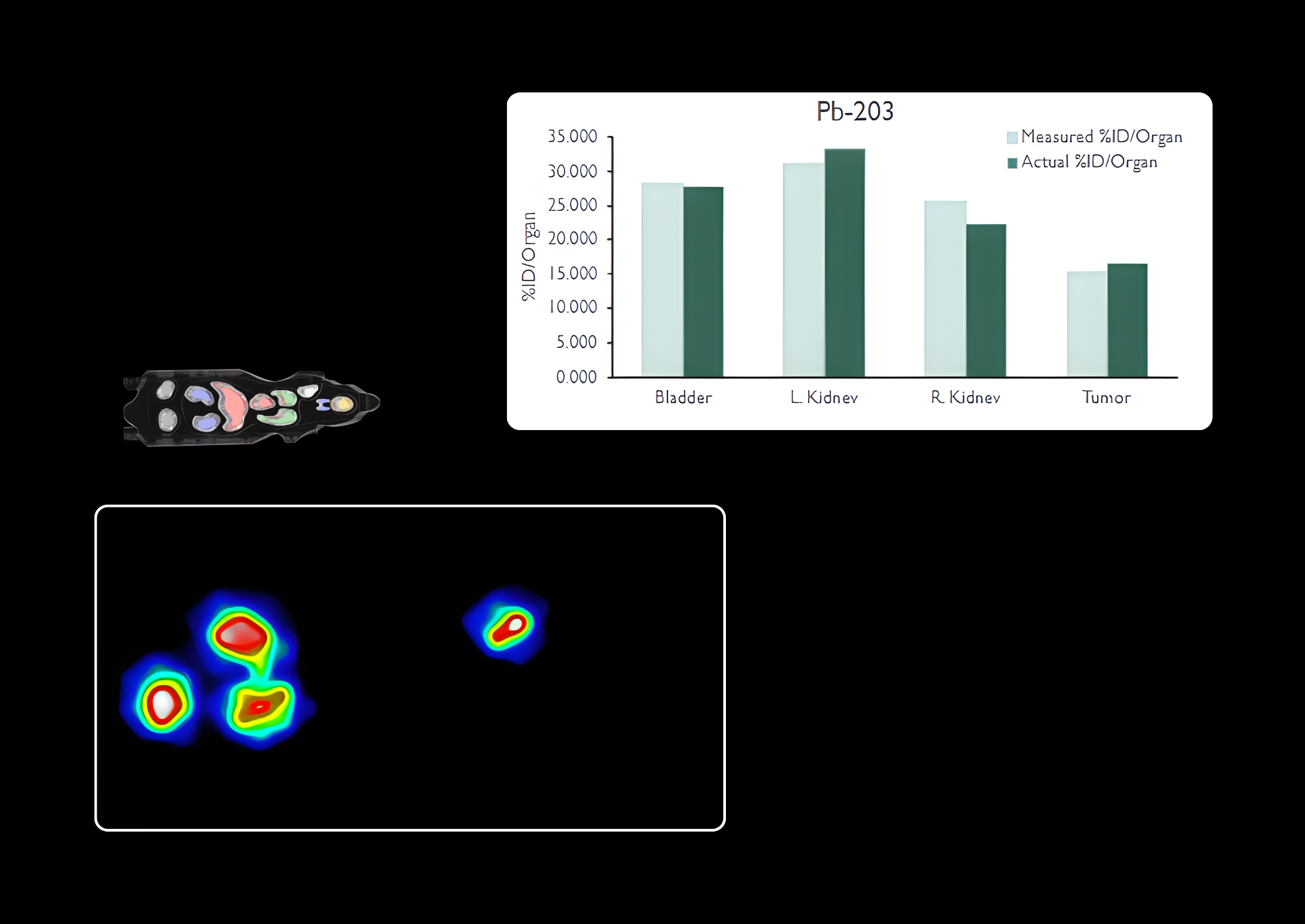
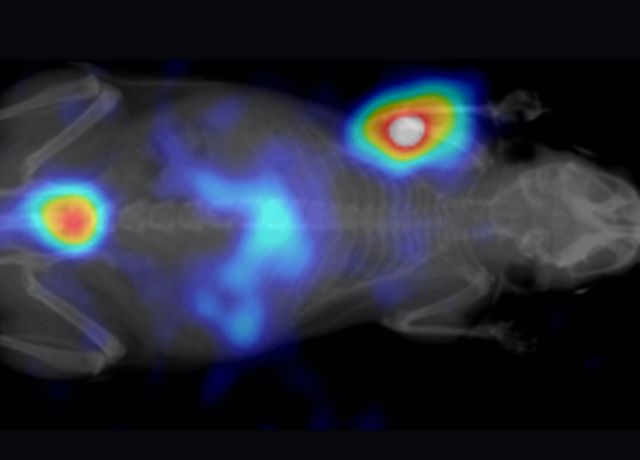
Real-time, in vivo rodent imaging, allows researchers to observe and monitor several normal and abnormal biological processes. Data collected using the eyes™ series, provides crucial initial insights and generate quantitative results that, in combination with the Visual | eyes™ interface, compose an essential platform for every preclinical laboratory.
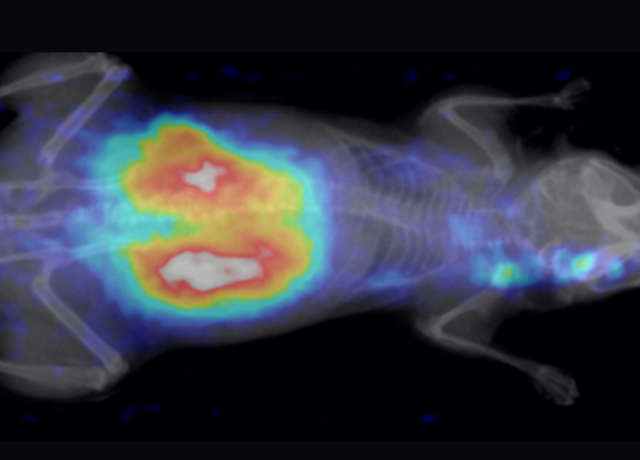
Oncology
Non-invasively assess your agent's targeting properties, real-time monitor drug delivery and track tumor progression.
Infection, Inflammation
Acquire detailed insights into disease mechanisms, enhance more accurate diagnostics while supporting the development or improvement of new or already existing therapeutics.

Protocol optimization
Test different animal preparation conditions, drug concentrations and administration routes to optimize your protocols.

Quick insights
Scan the same mouse at multiple time points to determine the optimal moments for 3D imaging. Conduct super-fast QC to exclude faulty injected subjects from further and more complex studies.